Cell Growth Embryogenesis
Identification of angiogenic activity and the cloning and expression of platelet derived endothelial cell growth factor.

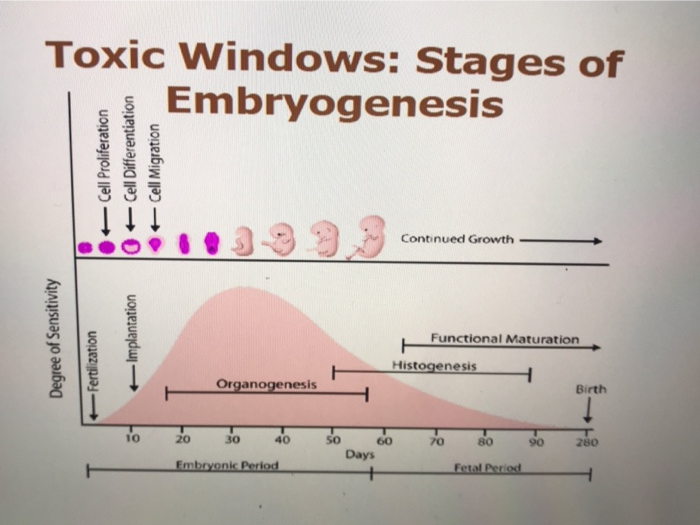
Cell growth embryogenesis. In biological terms the development of the human body entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. No endosperm or seed coat is formed around a somatic embryo. The below mentioned article provides a study note on somatic embryogenesis. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression cell growth and cellular differentiation.
Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis refers to the development and formation of the human embryoit is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In mammals the term refers chiefly to early stages of prenatal development whereas the terms fetus and fetal development describe later stages. Chapter 1 showed that the body plan of the embryo ie the apical basal polarity and the demarcation of the embryonic organs and tissue layers is laid down during early embryogenesisembryonic organs consist of the root and shoot apices the intervening root shoot axis and cotyledons one. Somatic embryos are formed from plant cells that are not normally involved in the development of embryos ie.
Lack of response to serum growth factors. Embryonic development also embryogenesis is the process by which the embryo forms and develops. Human embryogenesis is completed in two stages. Somatic embryogenesis is a procedure whereby a cell or group of cells from somatic tissue forms an embryo.
It is characterized by the process of cell division and cellular differentiation that occurs during the early stages of development. Somatic embryogenesis is an artificial process in which a plant or embryo is derived from a single somatic cell. The expansion of somatic embryos closely replicates the process of zygotic embryo formation. Somatic embryogenesis mostly occurs indirectly via a superseding callus phase or directly from early explants han et al 2011.
Somatic embryogenesis is the process in which a single cell or a small group of cells follow a developmental pathway that leads to reproducible regeneration of non zygotic embryos which are capable of producing a complete plant. A group of bioactive hormone like chemicals derived from fatty acids that have a wide variety of biological effects including roles in inflammation platelet aggregation vascular smooth muscle dilation and constriction cell growth protection of from acid in the stomach and many more. Ishikawa f miyazono k hellman u drexler h wernstedt c hagiwara k usuki k takaku f risau w heldin ch. Srivastava in plant growth and development.