Cell Growth Wound
Overview of the roles of growth factors in wound healing and their clinical applications for chronic wound treatment is also provided.
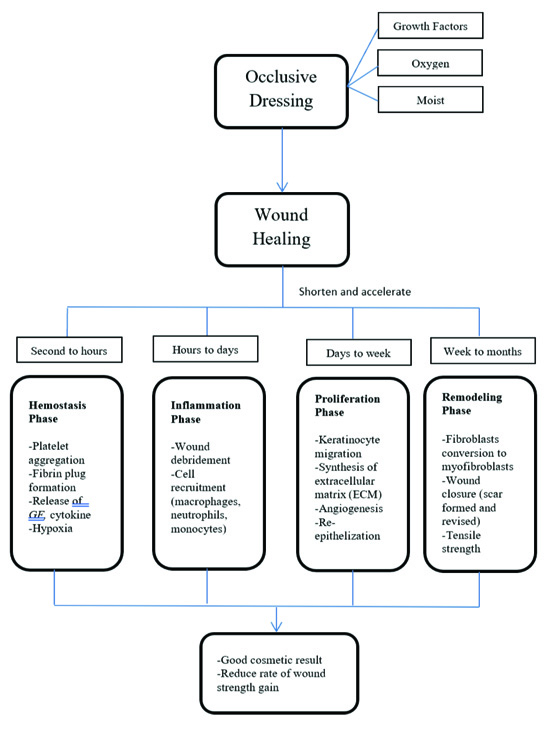
Cell growth wound. Growth factors represent the intercellular signaling that orchestrates the complex sequence of cell migration division differentiation and protein expression during wound healing. Nonhealing wounds contain high levels of il1 il6 and mmps and an abnormally high mmptimp ratio. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes hbm msc ex are a promising source for cell free therapy and skin regeneration. The 8 major families of growth factors are expressed in varying levels by the cells involved with healing.
Inflammatory cells and stromal cells secrete growth factors at the. The growth of tissue around the wound site is a result of the migration of cells and collagen deposition by these cells. Placental growth factor plgf is a proangiogenic molecule that is upregulated during wound healing. This growth factor acts by binding and activating the vegfr1.
This is achieved by the highly regulated process of cell. In unicellular organisms cell division is the means of reproduction. In multicellular organisms it is the means of tissue growth and maintenance. These results suggest potential therapeutic function in treatment of diabetic wounds.
Fibroblasts from chronic wounds do not respond to chronic wound fluid probably because the fibroblasts of these wounds have lost the receptors that respond to cytokines and growth factors. In the skin this growth factor is expressed by keratinocytes and by endothelial cells. Basket weave orientation of collagen is characteristic of normal skin whereas aligned collagen fibers lead to significant scarring. In this study we investigated the cell regeneration effects and its underlying mechanism of hbm msc ex on cutaneous wound.
180 25812587 2008. Survival of the eukaryotes depends upon interactions between many cell types and it is essential that a balanced distribution of types be maintained. Growth factors released in the traumatized area promote cell migration into the wound area chemotaxis stimulate the growth of epithelial cells and fibroblasts mitogenesis initiate the formation of new blood vessels angiogenesis and stimulate matrix formation and remodeling of the affected region. Mesenchymal stem cells are recruited into wounded skin and contribute to wound repair by transdifferentiation into multiple skin cell type.
Wound healing and its associated complications wound healing is a complex physiological process involving the interplay among various types of cells growth factors ecm components and proteinases 10. Cutaneous wound healing represents a morphogenetic response to injury and is designed to restore anatomic and physiological function.